The Two Variances in Direct Materials Cost Are
The difference between actual costs and standard or budgeted costs is typically explained by two separate variances. Causes for Direct Material Cost Variance.

Static Budget Variances Managerial Accounting Kavan Ingram I Like This Video For Static Budget Variance Because Budgeting Managerial Accounting Flexibility
This is happened due to.
. What are the two variances between the actual cost and the standard cost for direct materials. The direct material variance is comprised of two other variances which are. How do you determine the material cost variance.
Favorable variances result when actual costs are less than standard costs and vice versa. Note that both approachesthe direct materials quantity variance calculation and the alternative calculationyield the same result. Direct material cost variance is caused due to the following reasons.
Change in the mix of more than one type of materials in the process of manufacture. Change increase decrease in the quantity of materials used. Why do variances occur for direct materials and direct labor.
The direct material variance is comprised of two other variances which are noted below. Enter a favorable variance as a. 410 hrs Standard Quantity SQ 7x20000 140000 sq.
The direct material price variance can be calculated as follows. 11400 direct labour hours were worked at a cost of 142500. Change increase decrease in the price of materials.
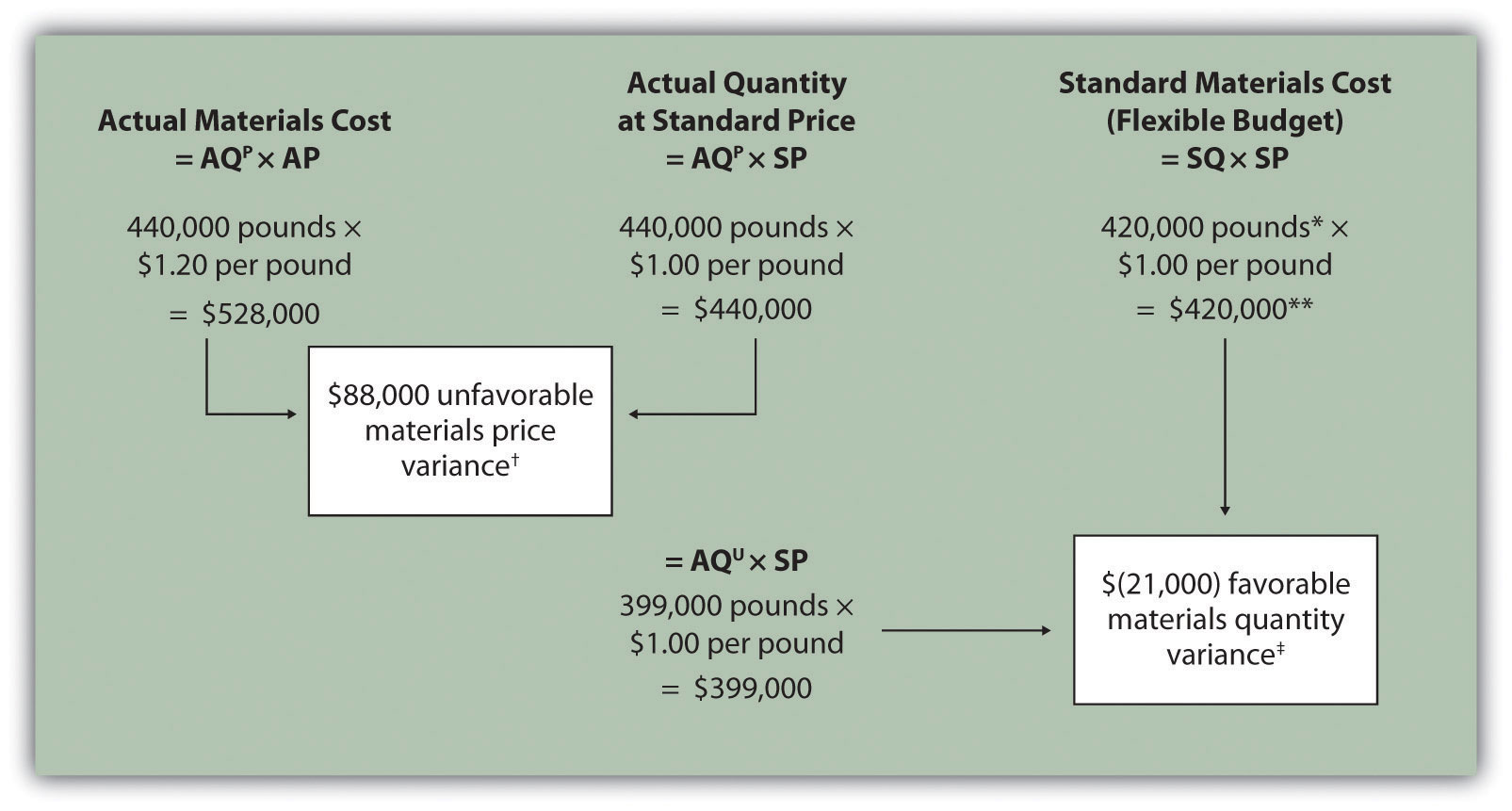
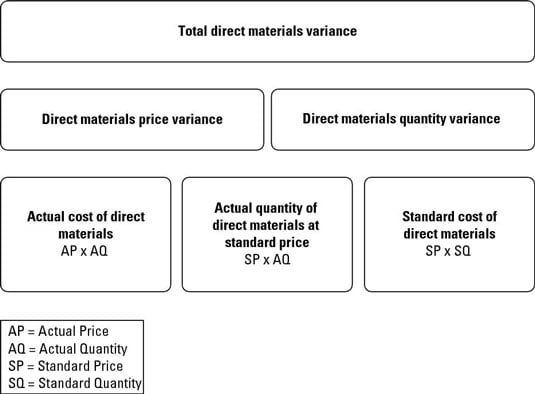
The direct material variance is the difference between the standard cost of materials resulting from production activities and the actual costs incurred. This is the difference between the actual cost incurred for direct materials and the expected or standard cost of those materials. The two direct materials variances are the materials price variance and the materials quantity variance.
What is a Material Variance. The materials price variance and materials quantity variance. Materials quantity variance AQ U SQ SP 399 000 42 0000 1 00 21 000 favorable.
Actual quantity purchased Standard price - Actual price Direct materials price variance. When a company makes a product and compares the actual materials cost to the standard materials cost the result is the total direct materials cost variance. What are the two variances between the actual cost and the standard cost for direct materials.
The purchasing department would be responsible for the price variance while the production department would be responsible for the quantity variance. Material Variance Related to Materials. Cost Variance Actual Cost x Actual Quantity Standard Cost x Actual Quantity Actual Cost Standard Cost x Actual Quantity AC-SC x AQ Direct Direct Materials Labor Actual Cost AC 105 sq.
To compute the direct labor price variance subtract the actual hours of direct labor at standard rate 43200 from the actual cost of direct labor 46800 to get a 3600 unfavorable variance. Direct Material Price Variance. The direct material quantity is computed as follows.
Your email address will not be published. Actual Quantity 050 times Actual Price 900 and Actual Quantity 050 times Standard Price 700 combine to point to Second row box. A Calculate Direct materials price and quantity variances.
Ft 1300 hr Standard Cost SC 110 sq. To compute the direct materials price variance subtract the actual cost of direct materials 297000 from the actual quantity of direct materials at standard price 310500. Combining the two variances can produce one overall total direct materials cost variance.
Direct Material Price Variance Standard price per unit of direct materials Actual price per unit of direct materials x Actual quantity of direct materials used. This difference comes to a 13500 favorable variance meaning that the company saves 13500 by buying direct materials for 990 rather than the original standard price of 1035. Ft 1200 Actual Quantity AQ 146000 sq.
Determine the direct materials price variance direct materials quantity variance and total direct materials cost variance. The Direct Material Variance based on actual cost and standard costs are divided into the following two categories. The two variances are the variable factory overhead and the fixed factory overhead.
Materials quantity variance AQU SQ SP. Direct Materials cost variance For instance if materials costs are higher than expected the direct material cost variance will be unfavorable. 40 or 40 Unfavorable In this case the actual price per unit of materials is 900 the standard price per unit of materials is 700 and the actual quantity purchased is 20 pounds.
Business Accounting QA Library Direct Materials Variances The following data relate to the direct materials cost for the production of 2300 automobile tires. Direct Material Price Variance 100 U. Direct Materials Price Variance 900 700 20 lbs.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply. Actual Quantity 50 times Standard Price 700 and Standard Quantity 025 times Standard Price 700 combine to point to Second row box. The formula approach for this variance is as follows.
The direct material price variance is the difference between standard cost and the actual cost for the actual quantity of material used for production. Material variance has two definitions one relating to direct materials and the other to the size of a variance. 20000 grams of this was still in inventory at the end of the month.
Total Direct Material Variance equals Actual Quantity times Actual Price minus. It is customary to calculate and report these two variances separately so that management can determine if variances are. 15000 ft 2 1000 - 945 8250 F.
Direct Materials efficiency variance For instance if it is taking more raw materials to assemble a product than expected the direct material efficiency variance will be unfavorable. 165000 grams were purchased at a cost of 104000. They are noted below.
Total Direct Materials Cost Variance. B Calculate Direct. Production data for May are.
What are the two variances between the actual cost and the standard cost for direct materials. The variable factory overhead controllable variance results from incurring total amount of variable factory overhead cost greater or less than the amount budgeted for the level of operations achieved. Alternatively we can use the formula approach to compute direct material price variance.
This is the difference between the standard and actual cost per unit of the direct materials purchased multiplied by the standard number of units expected to be used in the production process.

No comments for "The Two Variances in Direct Materials Cost Are"
Post a Comment